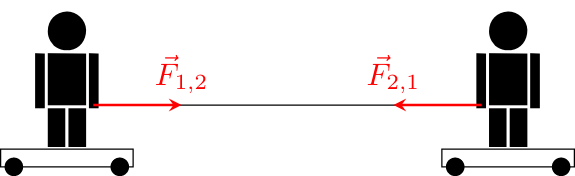Newton's Laws
There are 3 laws of Newton which are also called axioms because currently they cannot be derived from any other more fundamental principle. These 3 laws are usually formulated as follows:Newton's Laws
If an object in outer space is accelerated up to a specific velocity, it continues to move with that speed without bending its trajectory. Objects moving on the earth, however, experience many different frictions such as air resistance or surface frictions. In this case, the resulting decelerates the object which finally leads to a speed loss until the body comes to rest.
For example, if a person drives a car on the street and wants to make the car move at a constant speed, then it is necessary to constantly press the gas pedal, in order to compensate for the air resistance and surface friction between the tires and the street, as well as inner frictions of the engine.
Newton's second law matches exactly with our daily experiences. The harder a ball is kicked, the larger is its final speed after the acceleration has taken place. Furthermore, it is much easier to throw a ping pong ball than a heavy medicine ball.
Newton's third law can be experimentally shown with 2 people standing on different skateboards and holding the ends of a rope in their hands. If one person pulls his end towards himself, both skateboards move towards their center. If both people have approximately the same mass, they meet exactly in the middle.1. If no force acts on a body, then it remains in its position or moves with a constant speed: \[F = 0 \Rightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l} v = 0\\ v = \mathrm{const}\end{array}\right.\] 2. The change in the speed of an object is directly proportional to the force that acts on that body: \[\vec{F} = m\vec{a}\] 3. If one body acts a force on another body, the first one also experiences a force with the same magnitude but in the opposite direction. This axiom is therefore often called the action-reaction law.
This page contains 385 words and 2318 characters.
Last modified: 2022-10-01 17:07:28 by mustafa